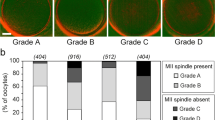
Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether spindle visualization using polarized light microscopy (PLM) can assist in identifying unfertilized oocytes prior to early rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection (R-ICSI).
Methods
This retrospective cohort study included 356 early R-ICSI cycles, of which 24 were excluded from the analysis. The remaining 332 cycles were divided into study group and control group based on whether spindle observation had been performed before early R-ICSI. The fertilization rate, embryo development, and clinical outcome were compared between the two groups.
Results
Of the 356 participants included, 332 completed follow-up analysis. The study group demonstrated a significantly higher normal fertilization rate (82.55% vs. 71.49%, P < 0.01) and a lower 3PN rate (3.17% vs. 8.89%, P < 0.01) after following R-ICSI. For oocytes without visible spindles in the study group or those with fragmented polar bodies in the control group, in vitro fertilization (IVF) was performed, resulting in a higher normal fertilization rate in the study group (53.37% vs. 36.43%, P < 0.01). However, there was no significant difference between the two groups in terms of embryo development and implantation potential. In the high-age subgroup (over 35 years old), the normal cleavage rate was significantly higher in the spindle examination group compared to the non-observation group (38.60% vs. 22.47%, P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Utilizing PLM for spindle observation can effectively identify oocytes suitable for early R-ICSI to improve fertilization outcomes and optimize embryo development in women over 35 years old.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on request.
References
Liu J, Zhang X, Yang Y, Zhao J, Hao D, Zhang J, Liu Y, Wu W, Wang X. Long-time vs. short-time insemination of sibling eggs. Exp Ther Med. 2016;12(6):3756–60. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2016.3827.
Combelles CM, Morozumi K, Yanagimachi R, Zhu L, Fox JH, Racowsky C. Diagnosing cellular defects in an unexplained case of total fertilization failure. Hum Reprod. 2010;25(7):1666–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deq064.
Nagy ZP, Joris H, Liu J, Staessen C, Devroey P, Van Steirteghem AC. Intracytoplasmic single sperm injection of 1-day-old unfertilized human oocytes. Hum Reprod. 1993;8(12):2180–4. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138000.
Pongsuthirak P. Comparison of embryonic competence and clinical outcomes between early and late cumulus cell removal for in vitro fertilization. Clin Exp Reprod Med. 2021;48(4):362–7. https://doi.org/10.5653/cerm.2021.04497.
Ming L, Liu P, Qiao J, Lian Y, Zheng X, Ren X, Huang J, Wu Y. Synchronization between embryo development and endometrium is a contributing factor for rescue ICSI outcome. Reprod Biomed Online. 2012;24(5):527–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.02.001.
Huang B, Qian K, Li Z, Yue J, Yang W, Zhu G, Zhang H. Neonatal outcomes after early rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection: an analysis of a 5-year period. Fertil Steril. 2015;103(6):1432–7.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.02.026.
Zeng J, Yao Z, Zhang Y, Tian F, Liao T, Wu L, Li Y. Fertilization and neonatal outcomes after early rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a retrospective analysis of 16,769 patients. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2022;306(1):249–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-022-06445-z.
Xiong S, Han W, Liu JX, Zhang XD, Liu WW, Liu H, Huang GN. Effects of cumulus cells removal after 6 h co-incubation of gametes on the outcomes of human IVF. J Assist Reprod Gen. 2011;28(12):1205–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-011-9630-9.
Jiang L, Qian Y, Chen X, Ji X, Ou S, Li R, Yang D, Li Y. Effect of early rescue ICSI and split IVF-ICSI in preventing low fertilization rate during the first ART cycle: a real-world retrospective cohort study. Reprod Med Biol. 2022;21(1):e12420. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmb2.12420.
Moon JH, Son WY, Henderson S, Mahfoudh A, Dahan M, Holzer H. Spindle examination in unfertilized eggs using the polarization microscope can assist rescue ICSI. Reprod Biomed Online. 2013;26(3):280–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2012.10.019.
Guo Y, Liu W, Wang Y, Pan J, Liang S, Ruan J, Teng X. Polarization microscopy imaging for the identification of unfertilized oocytes after short-term insemination. Fertil Steril. 2017;108(1):78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2017.05.009.
Holubcová, Z, Kyjovská, D, Martonová, M, Páralová, D, Klenková, T, Kloudová, S. Human egg maturity assessment and its clinical application. J Vis Exp. 2019;(150). https://doi.org/10.3791/60058.
The Istanbul consensus workshop on embryo assessment: proceedings of an expert meeting. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(6):1270–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/der037.
Yang ST, Shi JX, Gong F, Zhang SP, Lu CF, Tan K, Leng LZ, Hao M, He H, Gu YF, Lu GX, Lin G. Cleavage pattern predicts developmental potential of day 3 human embryos produced by IVF. Reprod Biomed Online. 2015;30(6):625–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.02.008.
Yang SH, Wu CH, Chen YC, Yang CK, Wu TH, Chen PC, Tsai HD. Effect of morphokinetics and morphological dynamics of cleavage stage on embryo developmental potential: a time-lapse study. Taiwan J Obstet Gyne. 2018;57(1):76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2017.12.013.
Barrie A, Homburg R, McDowell G, Brown J, Kingsland C, Troup S. Preliminary investigation of the prevalence and implantation potential of abnormal embryonic phenotypes assessed using time-lapse imaging. REPROD BIOMED ONLINE. 2017;34(5):455–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2017.02.011.
Gardner DK, Lane M, Stevens J, Schlenker T, Schoolcraft WB. Blastocyst score affects implantation and pregnancy outcome: towards a single blastocyst transfer. Fertil Steril. 2000;73(6):1155–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0015-0282(00)00518-5.
Xue Y, Tong X, Jiang L, Zhu H, Yang L, Zhang S. Effect of cumulus cell removal 4 h post-insemination on fertilization and embryo quality: a prospective randomized sibling-oocyte study. J Assist Reprod Gen. 2013;30(8):1049–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-013-0049-3.
Zhou L, Wang J, Xiao L, Sun H, Wang Y, Geng L, Hao G, Zhang C, Xu L, Qian W. Differential effects of short co-incubation of gametes and early removal of cumulus cells in patients with different fertilizing capabilities. Reprod Biomed Online. 2016;32(6):591–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.02.010.
Cao S, Wu X, Zhao C, Zhou L, Zhang J, Ling X. Determining the need for rescue intracytoplasmic sperm injection in partial fertilisation failure during a conventional IVF cycle. Andrologia. 2016;48(10):1138–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12551.
De Santis L, Cino I, Rabellotti E, Calzi F, Persico P, Borini A, Coticchio G. Polar body morphology and spindle imaging as predictors of oocyte quality. Reprod Biomed Online. 2005;11(1):36–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61296-5.
Zhou W, Fu L, Sha W, Chu D, Li Y. Relationship of polar bodies morphology to embryo quality and pregnancy outcome. Zygote. 2016;24(3):401–7. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0967199415000325.
Tilia L, Venetis C, Kilani S, Cooke S. Chapman, M, Is oocyte meiotic spindle morphology associated with embryo ploidy? A prospective cohort study. Fertil Steril. 2016;105(4):1085–1092.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.12.018.
Tomari H, Honjo K, Kunitake K, Aramaki N, Kuhara S, Hidaka N, Nishimura K, Nagata Y, Horiuchi T. Meiotic spindle size is a strong indicator of human oocyte quality. Reprod Med Biol. 2018;17(3):268–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/rmb2.12100.
Asa E, Tabatabaee R, Farrokhi A, Nejatbakhsh R. Relationship between meiotic spindles visualization and intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcomes in human oocytes. Anat Cell Biol. 2017;50(1):26–32. https://doi.org/10.5115/acb.2017.50.1.26.
Tepla O, Topurko Z, Jirsova S, Moosova M, Fajmonova E, Cabela R, Komrskova K, Kratochvilova I, Masata J. Timing of ICSI with respect to meiotic spindle status. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;24(1):105. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms24010105.
Korkmaz C, Tekin YB, Sakinci M, Ercan CM. Effects of maternal ageing on ICSI outcomes and embryo development in relation to oocytes morphological characteristics of birefringent structures. Zygote. 2015;23(4):550–5. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0967199414000197.
Holubcová Z, Kyjovská D, Martonová M, Páralová D, Klenková T, Otevřel P, Štěpánová R, Kloudová S, Hampl A. Egg maturity assessment prior to ICSI prevents premature fertilization of late-maturing oocytes. J Assist Reprod Gen. 2019;36(3):445–52. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1393-0.
Acknowledgements
We extend our sincere appreciation to all colleagues who were responsible for case recruitment, technical procedures, data documentation, and statistical evaluation.
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing, Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (Grant Number: CSTB2022 NSCQ-MSX0253).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG.: designed research, analyzed data, and wrote the manuscript. JHZ., SX., and JW.: recorded data and followed up the outcomes. XWH. and HYL.: implemented the technical operation. WH. and JXL.: recruited patients and collected informed consent. GNH.: guided the experiment. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Ethics Committee Review Board of the Chongqing Health Center for Women and Children on 22 June 2021 (Approval No. 2021-RGI- 02). All patients provided informed consent prior to inclusion in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 15.3 KB)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Zhu, J., Xiong, S. et al. Spindle observation aids decision-making for early rescue ICSI. J Assist Reprod Genet (2025). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-025-03474-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-025-03474-w